Χαρτογράφηση του Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας
6.1. Εισαγωγή
Το οικοσύστημα της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας στον σημερινό κόσμο είναι εξαιρετικά σημαντικό και αναπτύσσεται με ταχείς ρυθμούς. Η αυξανόμενη περιβαλλοντική ευαισθητοποίηση της κοινωνίας και η ανάγκη μείωσης των αρνητικών ανθρώπινων επιπτώσεων στο περιβάλλον καθιστούν τις πράσινες επιχειρήσεις όλο και πιο σημαντικές. Το οικοσύστημα της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας είναι ζωτικής σημασίας λόγω του εύρους των οφελών που επιφέρει στην κοινωνία και το περιβάλλον.
Αυτή η ενότητα επικεντρώνεται στο Οικοσύστημα της Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας. Θα παρουσιαστούν οι βασικοί ορισμοί που σχετίζονται με το θέμα αυτό και θα εξεταστεί το ζήτημα της χαρτογράφησης του Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας, δηλαδή τι είναι στην πραγματικότητα, πώς μοιάζει και πώς μπορεί να δημιουργηθεί. Θα παρουσιάσουμε επίσης υπάρχοντα παραδείγματα αυτού του τύπου ή παρόμοιων χαρτών.
6.2. Απλοί ορισμοί
Ας δούμε μερικούς βασικούς ορισμούς που θα μας βοηθήσουν να κατανοήσουμε καλύτερα το θέμα της ενότητας.
Πράσινη Επιχειρηματικότητα – Η πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα αναφέρεται στη δημιουργία και ανάπτυξη βιώσιμων επιχειρήσεων που στοχεύουν στην αντιμετώπιση περιβαλλοντικών και κοινωνικών προκλήσεων. Οι επιχειρήσεις αυτές επικεντρώνονται στη δημιουργία καινοτόμων λύσεων σε περιβαλλοντικά προβλήματα, όπως η μείωση των εκπομπών διοξειδίου του άνθρακα, η διατήρηση των φυσικών πόρων και η προώθηση των ανανεώσιμων πηγών ενέργειας.
Πράσινος Επιχειρηματίας – Οι πράσινοι επιχειρηματίες συχνά συνδυάζουν το πάθος τους για τη βιωσιμότητα με την επιχειρηματική οξυδέρκεια για να δημιουργήσουν επιχειρήσεις που είναι οικονομικά βιώσιμες, ενώ παράλληλα έχουν θετικό αντίκτυπο στο περιβάλλον και την κοινωνία. Μπορεί να δραστηριοποιούνται σε διάφορους κλάδους, όπως η καθαρή ενέργεια, η βιώσιμη γεωργία, ο οικολογικός τουρισμός, η διαχείριση αποβλήτων και οι πράσινες μεταφορές.
Επιχειρηματικό Οικοσύστημα – Το επιχειρηματικό οικοσύστημα είναι μια συλλογή διαφορετικών ατόμων που μπορεί να είναι δυνητικοί ή υφιστάμενοι επιχειρηματίες, οι οργανισμοί που υποστηρίζουν την επιχειρηματικότητα, οι οποίοι μπορεί να είναι εταιρείες, επενδυτές επιχειρηματικών κεφαλαίων, επιχειρηματικοί άγγελοι και τράπεζες, καθώς και ιδρύματα όπως πανεπιστήμια, οργανισμοί του δημόσιου τομέα, και οι επιχειρηματικές διαδικασίες που λαμβάνουν χώρα εντός του οικοσυστήματος, όπως ο ρυθμός δημιουργίας επιχειρήσεων, ο αριθμός των εταιρειών με υψηλό δυναμικό ανάπτυξης, οι κατά συρροή επιχειρηματίες και οι επιχειρηματικές φιλοδοξίες τους.
Οι παραπάνω ορισμοί και η κατανόησή τους αποτελούν βασικό μέρος της κατανόησης της έννοιας της χαρτογράφησης του Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας και των στοιχείων που πρέπει να περιλαμβάνονται κατά τη χαρτογράφηση των πράσινων επιχειρηματιών.
6.3. Τι είναι το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας
Το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας αναφέρεται στα διάφορα στοιχεία και τους ενδιαφερόμενους φορείς που εμπλέκονται στη δημιουργία και την προώθηση της βιώσιμης και φιλικής προς το περιβάλλον επιχειρηματικότητας και καινοτομίας. Το οικοσύστημα περιλαμβάνει νεοσύστατες επιχειρήσεις, επενδυτές, φορείς χάραξης πολιτικής, ερευνητικά ιδρύματα, οργανισμούς υποστήριξης και άλλους ενδιαφερόμενους που εργάζονται για τον κοινό στόχο της δημιουργίας μιας βιώσιμης οικονομίας.
Το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας αποτελείται από διάφορα βασικά στοιχεία:
- Πράσινες Νεοφυείς Επιχειρήσεις: Πρόκειται για επιχειρήσεις που δημιουργούν καινοτόμα προϊόντα, υπηρεσίες και τεχνολογίες που προωθούν τη βιωσιμότητα και αντιμετωπίζουν περιβαλλοντικές προκλήσεις.
- Επενδυτές: Πρόκειται για άτομα ή οργανισμούς που παρέχουν χρηματοδότηση σε πράσινες νεοσύστατες επιχειρήσεις και υποστηρίζουν τη βιώσιμη επιχειρηματικότητα.
- Υπεύθυνοι χάραξης πολιτικής: Πρόκειται για κυβερνητικούς αξιωματούχους και οργανισμούς που δημιουργούν πολιτικές και κανονισμούς που υποστηρίζουν την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα και την βιωσιμότητα.
- Ερευνητικά ιδρύματα: Πανεπιστήμια, ερευνητικά κέντρα και εργαστήρια που διεξάγουν έρευνα για πράσινες τεχνολογίες, προϊόντα και υπηρεσίες και παρέχουν πολύτιμες γνώσεις και εμπειρογνωμοσύνη στους επιχειρηματίες.
- Οργανώσεις Υποστήριξης: Πρόκειται για φορείς που παρέχουν πόρους, καθοδήγηση και υποστήριξη σε πράσινες νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις και επιχειρηματίες, όπως θερμοκοιτίδες, επιταχυντές και οργανώσεις δικτύωσης.
- Μη Κυβερνητικές Οργανώσεις (ΜΚΟ): Περιβαλλοντικές οργανώσεις και ομάδες προάσπισης που παρέχουν υποστήριξη, καθοδήγηση και πόρους σε πράσινους επιχειρηματίες και προωθούν πρωτοβουλίες βιωσιμότητας.
- Καταναλωτές: Πρόκειται για άτομα και οργανισμούς που αγοράζουν προϊόντα και υπηρεσίες από πράσινες νεοσύστατες επιχειρήσεις και υποστηρίζουν την ανάπτυξη μιας βιώσιμης οικονομίας.
Το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας είναι απαραίτητο για την προώθηση της βιώσιμης οικονομικής ανάπτυξης και την αντιμετώπιση των περιβαλλοντικών προκλήσεων. Συνδέοντας και υποστηρίζοντας πράσινες νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις και επιχειρηματίες, οι υπεύθυνοι χάραξης πολιτικής, οι επενδυτές και άλλοι ενδιαφερόμενοι μπορούν να προωθήσουν την καινοτομία και να δημιουργήσουν νέες ευκαιρίες για τη βιώσιμη ανάπτυξη.
Υπάρχουν διάφορα στατιστικά στοιχεία που παρέχουν πληροφορίες για το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας σε όλο τον κόσμο. Ακολουθούν ορισμένα παραδείγματα:
- Επενδύσεις: Σύμφωνα με έκθεση από την Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment, το 2020, οι παγκόσμιες επενδύσεις στη δυναμικότητα των ανανεώσιμων πηγών ενέργειας ανήλθαν σε 303,5 δισεκατομμύρια δολάρια, σημειώνοντας αύξηση 2% σε σχέση με το 2019. Αυτό περιλαμβάνει επενδύσεις σε αιολικές, ηλιακές, υδροηλεκτρικές και άλλες ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας.
- Νεοφυείς Επιχειρήσεις: Σύμφωνα με έκθεση του Cleantech Group, υπήρχαν 12.852 νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις καθαρής τεχνολογίας παγκοσμίως από το 2019, με την πλειονότητα να βρίσκεται στη Βόρεια Αμερική και την Ευρώπη.
- Κυβερνητική υποστήριξη: Σύμφωνα με έκθεση του the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), από το 2020, 136 χώρες είχαν στόχους για τις ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας και 91 χώρες είχαν πολιτικές για την υποστήριξη της ανάπτυξης των ανανεώσιμων πηγών ενέργειας.
- Δημιουργία θέσεων εργασίας: Σύμφωνα με έκθεση του International Labour Organization (ILO), ο τομέας των ανανεώσιμων πηγών ενέργειας δημιούργησε 11 εκατομμύρια νέες θέσεις εργασίας παγκοσμίως από το 2018, από 10,3 εκατομμύρια το 2017.
- Μέγεθος αγοράς: Σύμφωνα με έκθεση της Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction, η παγκόσμια αγορά πράσινων κτιρίων αποτιμάται σε 260 δισεκατομμύρια δολάρια το 2019, με προβλεπόμενο ρυθμό ανάπτυξης 10% ετησίως.
Όπως γίνεται αντιληπτό, τα στατιστικά αυτά στοιχεία καταδεικνύουν την ανάπτυξη και τις δυνατότητες του Οικοσυστήματος της Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας, με αυξανόμενες επενδύσεις, δραστηριότητα εκκίνησης, κυβερνητική στήριξη, δημιουργία θέσεων εργασίας και μέγεθος αγοράς. Ωστόσο, υπάρχουν επίσης προκλήσεις και εμπόδια για την ανάπτυξη αυτού του οικοσυστήματος, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της πρόσβασης σε χρηματοδότηση, των  ρυθμιστικών εμποδίων και των εμποδίων της αγοράς.
ρυθμιστικών εμποδίων και των εμποδίων της αγοράς.
Πηγή: https://img.freepik.com/free-photo/sustainable-development-goals-still-life_23-2150196661.jpg
6.4. Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας στην Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση
Η Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση (ΕΕ) προωθεί ενεργά την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα και την βιωσιμότητα μέσω διαφόρων πρωτοβουλιών, πολιτικών και προγραμμάτων χρηματοδότησης. Η ΕΕ έχει θέσει φιλόδοξους στόχους για τη μετάβαση σε μια οικονομία χαμηλών εκπομπών άνθρακα, κυκλική και αποδοτική ως προς τους πόρους, και η πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα διαδραματίζει κρίσιμο ρόλο στην επίτευξη αυτών των στόχων.
Η πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα αποτελεί σημαντική συνιστώσα των προσπαθειών της Ευρωπαϊκής Ένωσης για την προώθηση της βιωσιμότητας και την αντιμετώπιση της κλιματικής αλλαγής. Οι πράσινοι επιχειρηματίες στην ΕΕ διαδραματίζουν ζωτικό ρόλο στην ανάπτυξη και κλιμάκωση καινοτόμων τεχνολογιών και λύσεων για την αντιμετώπιση των περιβαλλοντικών προκλήσεων, δημιουργώντας παράλληλα οικονομικές ευκαιρίες. Αξιοποιούν την καινοτομία, τη συνεργασία και τις ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης για την ανάπτυξη και την κλιμάκωση βιώσιμων λύσεων που αντιμετωπίζουν τις περιβαλλοντικές προκλήσεις δημιουργώντας παράλληλα οικονομικές ευκαιρίες.
Το οικοσύστημα της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας στην ΕΕ περιλαμβάνει ένα ευρύ φάσμα ενδιαφερόμενων μερών, όπως νεοσύστατες επιχειρήσεις, επενδυτές, φορείς χάραξης πολιτικής, ερευνητικά ιδρύματα και οργανισμούς υποστήριξης. Η ΕΕ διαθέτει διάφορες πρωτοβουλίες και προγράμματα για τη στήριξη της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας, όπως :
- Horizon Europe: Το Horizon Europe είναι το μεγαλύτερο πρόγραμμα έρευνας και καινοτομίας της ΕΕ, με προϋπολογισμό 95,5 δισεκατομμυρίων ευρώ. Περιλαμβάνει ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης για έρευνα και καινοτομία σε τομείς όπως η κλιματική αλλαγή, η ενέργεια και η κυκλική οικονομία.
- Ευρωπαϊκή Πράσινη Συμφωνία: Η Ευρωπαϊκή Πράσινη Συμφωνία είναι ένας οδικός χάρτης για να καταστεί η οικονομία της ΕΕ βιώσιμη. Περιλαμβάνει, μεταξύ άλλων, πρωτοβουλίες και πολιτικές που σχετίζονται με την ενεργειακή απόδοση, τις ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας, την κυκλική οικονομία και τη βιώσιμη γεωργία.
- Ευρωπαϊκή Τράπεζα Επενδύσεων (EIB): Η EIB είναι ίδρυμα της ΕΕ για τον μακροπρόθεσμο δανεισμό, το οποίο παρέχει χρηματοδότηση για βιώσιμες υποδομές και πράσινα έργα. Υποστηρίζει επίσης την ανάπτυξη πράσινων ομολόγων και άλλων χρηματοπιστωτικών μέσων.
- Climate-KIC: Η Climate-KIC είναι η μεγαλύτερη σύμπραξη δημόσιου και ιδιωτικού τομέα της ΕΕ που επικεντρώνεται στην καινοτομία για το κλίμα. Υποστηρίζει νεοσύστατες επιχειρήσεις, ερευνητικά ιδρύματα και άλλους ενδιαφερόμενους φορείς που εργάζονται σε λύσεις για το κλίμα.
- Ευρωπαϊκό Ινστιτούτο Καινοτομίας και Τεχνολογίας (ΕΙΤ): Το ΕΙΤ είναι ένας οργανισμός της ΕΕ που υποστηρίζει την καινοτομία και την επιχειρηματικότητα σε τομείς όπως το κλίμα, η ενέργεια και η βιώσιμη κινητικότητα.
Σε γενικές γραμμές, το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας στην ΕΕ είναι καλά ανεπτυγμένο, με μια σειρά πρωτοβουλιών και προγραμμάτων για τη στήριξη νεοφυών επιχειρήσεων και επιχειρηματιών που εργάζονται πάνω σε βιώσιμες λύσεις. Η δέσμευση της ΕΕ για τη βιωσιμότητα και τη μετάβαση σε μια οικονομία χαμηλών εκπομπών διοξειδίου του άνθρακα παρέχει ένα ευνοϊκό περιβάλλον για την άνθηση της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας.
Το Οικοσύστημα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας στις χώρες της ΕΕ ποικίλλει ανάλογα με το επίπεδο ανάπτυξης της πράσινης οικονομίας, τη διαθεσιμότητα των πόρων και τις τοπικές πολιτικές και ρυθμίσεις. Ακολουθούν ορισμένα παραδείγματα Οικοσυστημάτων Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας σε διάφορες ευρωπαϊκές χώρες:
- Γερμανία: Η Γερμανία κατέχει ηγετική θέση στην πράσινη οικονομία, με ένα καλά αναπτυγμένο οικοσύστημα που υποστηρίζει την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα. Η χώρα δίνει μεγάλη έμφαση στην καινοτομία και την έρευνα, με πολλά πανεπιστήμια και ερευνητικά ιδρύματα να εστιάζουν στην βιωσιμότητα. Η Γερμανική κυβέρνηση παρέχει διάφορες ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης και φορολογικά κίνητρα για τους πράσινους επιχειρηματίες και υπάρχει μια ζωντανή κοινότητα νεοφυών επιχειρήσεων που επικεντρώνεται στις πράσινες τεχνολογίες.
- Σουηδία: Η Σουηδία έχει σημειώσει σημαντική πρόοδο στη μετάβαση σε μια οικονομία χαμηλών εκπομπών διοξειδίου του άνθρακα, με μεγάλη έμφαση στις ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας και τις βιώσιμες μεταφορές. Η χώρα διαθέτει ένα καλά ανεπτυγμένο οικοσύστημα που υποστηρίζει την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα, με διάφορες ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης, θερμοκοιτίδες και επιταχυντές που εστιάζουν στη βιωσιμότητα. Η σουηδική κυβέρνηση παρέχει επίσης φορολογικά κίνητρα και άλλες μορφές στήριξης για τις πράσινες επιχειρήσεις.
- Γαλλία: Η Γαλλία διαθέτει ένα αναπτυσσόμενο οικοσύστημα πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας, με έμφαση στην προώθηση της καινοτομίας και της βιώσιμης ανάπτυξης. Η χώρα διαθέτει πολλά πανεπιστήμια και ερευνητικά ιδρύματα που επικεντρώνονται στη βιωσιμότητα, ενώ η Γαλλική κυβέρνηση παρέχει διάφορες ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης και φορολογικά κίνητρα για τους πράσινους επιχειρηματίες. Η Γαλλία διαθέτει επίσης μια ζωντανή κοινότητα νεοφυών επιχειρήσεων που επικεντρώνεται στη βιωσιμότητα, με πολλές θερμοκοιτίδες και επιταχυντές που υποστηρίζουν τις πράσινες επιχειρήσεις.
- Ισπανία: Η Ισπανία διαθέτει έναν καλά ανεπτυγμένο τομέα ανανεώσιμων πηγών ενέργειας και ένα αναπτυσσόμενο οικοσύστημα για την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα. Η ισπανική κυβέρνηση παρέχει διάφορες ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης και φορολογικά κίνητρα για τους πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, ενώ δίνεται μεγάλη έμφαση στην προώθηση της βιωσιμότητας στην κοινότητα νεοφυών επιχειρήσεων της χώρας. Η Ισπανία διαθέτει επίσης πολλά πανεπιστήμια και ερευνητικά ιδρύματα που επικεντρώνονται στη βιωσιμότητα, παρέχοντας ευκαιρίες για συνεργασία και καινοτομία.
- Δανία: Η Δανία είναι πρωτοπόρος στις ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας και διαθέτει ένα καλά αναπτυγμένο οικοσύστημα για την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα. Η χώρα δίνει μεγάλη έμφαση στη βιωσιμότητα και την πράσινη καινοτομία, με πολλά πανεπιστήμια και ερευνητικά ιδρύματα να επικεντρώνονται σε αυτούς τους τομείς. Η δανέζικη κυβέρνηση παρέχει διάφορες ευκαιρίες χρηματοδότησης και φορολογικά κίνητρα για πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, ενώ υπάρχει μια ζωντανή κοινότητα νεοφυών επιχειρήσεων που επικεντρώνεται στη βιωσιμότητα.
 Τα Οικοσυστήματα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας στις χώρες της ΕΕ ποικίλλουν, αλλά πολλά από αυτά έχουν κοινά χαρακτηριστικά, όπως η εστίαση στην καινοτομία, η συνεργασία και η κυβερνητική στήριξη των πράσινων επιχειρήσεων. Η ανάπτυξη οικοσυστημάτων πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας στις ευρωπαϊκές χώρες είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για τη μετάβαση σε μια πιο βιώσιμη οικονομία με χαμηλές εκπομπές διοξειδίου του άνθρακα και τη δημιουργία οικονομικών ευκαιριών που υποστηρίζουν την περιβαλλοντική και κοινωνική ευημερία.
Τα Οικοσυστήματα Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας στις χώρες της ΕΕ ποικίλλουν, αλλά πολλά από αυτά έχουν κοινά χαρακτηριστικά, όπως η εστίαση στην καινοτομία, η συνεργασία και η κυβερνητική στήριξη των πράσινων επιχειρήσεων. Η ανάπτυξη οικοσυστημάτων πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας στις ευρωπαϊκές χώρες είναι ζωτικής σημασίας για τη μετάβαση σε μια πιο βιώσιμη οικονομία με χαμηλές εκπομπές διοξειδίου του άνθρακα και τη δημιουργία οικονομικών ευκαιριών που υποστηρίζουν την περιβαλλοντική και κοινωνική ευημερία.
Πηγή: https://www.pubaffairsbruxelles.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/bon-1.jpg
6.5. Χαρτογράφηση Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας
Η χαρτογράφηση Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας είναι μια οπτική αναπαράσταση των διαφόρων στοιχείων και των ενδιαφερομένων μερών που εμπλέκονται στη δημιουργία μιας βιώσιμης και ακμάζουσας πράσινης οικονομίας. Συνήθως περιλαμβάνει στοιχεία όπως πράσινες νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις, θερμοκοιτίδες, επιταχυντές, επενδυτές, φορείς χάραξης πολιτικής, ΜΚΟ, πανεπιστήμια και ερευνητικά ιδρύματα που εμπλέκονται στην προώθηση της φιλικής προς το περιβάλλον επιχειρηματικότητας και καινοτομίας.
Η χαρτογράφηση συμβάλλει στον εντοπισμό και τη σύνδεση των διαφόρων παραγόντων του οικοσυστήματος, στην επισήμανση των τομέων όπου μπορεί να υπάρχουν κενά ή ευκαιρίες και στην παρουσίαση επιτυχημένων παραδειγμάτων πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας. Μπορεί να χρησιμοποιηθεί ως εργαλείο για τους υπεύθυνους χάραξης πολιτικής, τους επενδυτές και τους επιχειρηματίες ώστε να κατανοήσουν τις βασικές συνιστώσες της πράσινης οικονομίας και να εντοπίσουν πιθανούς τομείς συνεργασίας και επενδύσεων.
Η δημιουργία της χαρτογράφησης ενός Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας περιλαμβάνει τον εντοπισμό και τη χαρτογράφηση των διαφόρων συνιστωσών του οικοσυστήματος που υποστηρίζει την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα. Ακολουθούν τα βήματα για τη δημιουργία της χαρτογράφησης ενός Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας:
- Προσδιορίστε τα ενδιαφερόμενα μέρη: Ξεκινήστε με τον εντοπισμό των βασικών ενδιαφερομένων στο οικοσύστημα της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας, συμπεριλαμβανομένων των επιχειρηματιών, των επενδυτών, των κυβερνητικών φορέων, των πανεπιστημίων, των ερευνητικών ιδρυμάτων, των ΜΚΟ και άλλων οργανισμών που ασχολούνται με τη βιωσιμότητα.
- Κατανοήστε τις αλληλεπιδράσεις: Χαρτογραφήστε τις αλληλεπιδράσεις μεταξύ των ενδιαφερομένων μερών και προσδιορίστε τον τρόπο με τον οποίο συνεργάζονται για τη δημιουργία ενός υποστηρικτικού οικοσυστήματος για την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα. Αυτό θα βοηθήσει στην κατανόηση της δυναμικής του οικοσυστήματος.
- Χαρτογραφήστε τους πόρους: Προσδιορίστε τους πόρους που είναι διαθέσιμοι στους πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της χρηματοδότησης, της καθοδήγησης, των ευκαιριών δικτύωσης, των θερμοκοιτίδων και καθώς των επιταχυντών και άλλων πόρων.
- Προσδιορίστε τις βασικές προκλήσεις: Κατανοήστε τις προκλήσεις που αντιμετωπίζουν οι πράσινοι επιχειρηματίες στο οικοσύστημα, όπως η πρόσβαση σε κεφάλαια, η έλλειψη εξειδικευμένου εργατικού δυναμικού, τα ρυθμιστικά εμπόδια και άλλα.
- Αναλύστε το οικοσύστημα: Αναλύστε τα δυνατά και αδύνατα σημεία του οικοσυστήματος, καταγράφοντας τις ευκαιρίες και τις απειλές και εντοπίζοντας τα κενά και τους τομείς προς βελτίωση.
- Δημιουργήστε τη χαρτογράφηση του οικοσυστήματος: Χρησιμοποιώντας τις πληροφορίες που συγκεντρώσατε, δημιουργήστε μια οπτική αναπαράσταση του οικοσυστήματος της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας. Αυτή μπορεί να έχει τη μορφή διαγράμματος ροής, διαγράμματος ή χάρτη που δείχνει τις σχέσεις μεταξύ των ενδιαφερομένων μερών, τους διαθέσιμους πόρους, τις προκλήσεις που αντιμετωπίζουν, καθώς και τις ευκαιρίες και τις απειλές.
- Ενημέρωση της χαρτογράφησης οικοσυστημάτων: Διατηρείτε τη χαρτογράφηση των οικοσυστημάτων ενημερωμένη, επανεξετάζοντας και επικαιροποιώντας τακτικά τις πληροφορίες με βάση τις αλλαγές στο οικοσύστημα.
Συνολικά, η δημιουργία μιας Χαρτογράφησης Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας προϋποθέτει την εις βάθος κατανόηση των ενδιαφερομένων μερών, των πόρων, των προκλήσεων και των ευκαιριών στο οικοσύστημα, καθώς και του τρόπου με τον οποίο αλληλεπιδρούν για την υποστήριξη της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας.
Είναι σημαντικό να σημειωθεί ότι τα συγκεκριμένα στοιχεία και οι αλληλεπιδράσεις τους στο πλαίσιο ενός οικοσυστήματος πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας μπορεί να διαφέρουν ανάλογα με την περιοχή, τον κλάδο και το τοπικό πλαίσιο.
Ακολουθούν ορισμένα βασικά στοιχεία που θα μπορούσατε να βρείτε σε μια Χαρτογράφηση Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας:
- Επιχειρηματίες και Νεοσύστατες Επιχειρήσεις: Ο πυρήνας του οικοσυστήματος, που αντιπροσωπεύει άτομα και ομάδες που αναπτύσσουν και δρομολογούν πράσινες επιχειρηματικές ιδέες και εγχειρήματα.
- Θερμοκοιτίδες και επιταχυντές: Οργανισμοί που παρέχουν υποστήριξη, καθοδήγηση και πόρους σε πράσινες νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις αρχικών σταδίων, συμπεριλαμβανομένης της καθοδήγησης, του χώρου εργασίας, των ευκαιριών χρηματοδότησης και της πρόσβασης σε δίκτυα.
- Πηγές χρηματοδότησης: Χρηματοπιστωτικά ιδρύματα, επενδυτές επιπτώσεων, επενδυτές επιχειρηματικών κεφαλαίων, άγγελοι-επενδυτές, πλατφόρμες crowdfunding και κρατικές επιχορηγήσεις που προσφέρουν κεφάλαια και επενδυτικές ευκαιρίες για πράσινες νεοφυείς επιχειρήσεις.
- Ερευνητικά ιδρύματα: Πανεπιστήμια, ερευνητικά κέντρα και εργαστήρια που διεξάγουν έρευνα σχετικά με τις πράσινες τεχνολογίες, τις βιώσιμες πρακτικές και τις περιβαλλοντικές λύσεις, παρέχοντας πολύτιμη τεχνογνωσία και γνώση στους επιχειρηματίες.
- Κυβερνητική Στήριξη και Πολιτικές: Κυβερνητικές πρωτοβουλίες, πολιτικές και κανονισμοί που προωθούν τη βιωσιμότητα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων φορολογικών κινήτρων, επιχορηγήσεων, επιδοτήσεων και προτιμήσεων προμηθειών για πράσινες επιχειρήσεις.
- Μη Κυβερνητικές Οργανώσεις (ΜΚΟ) και Δίκτυα: Περιβαλλοντικές οργανώσεις, ΜΚΟ με επίκεντρο τη βιωσιμότητα και δίκτυα που παρέχουν υποστήριξη, καθοδήγηση και υπεράσπιση για πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, προωθώντας πρακτικές περιβαλλοντικής διαχείρισης και βιωσιμότητας.
- Βιομηχανικές ενώσεις και συστάδες: Ενώσεις και δίκτυα που συγκεντρώνουν πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, επαγγελματίες και ενδιαφερόμενους φορείς σε συγκεκριμένες βιομηχανίες ή τομείς, προωθώντας τη συνεργασία, την ανταλλαγή γνώσεων και την πρόσβαση στην αγορά..
- Ευκαιρίες αγοράς και Ζήτηση αγοράς: Αύξηση της ζήτησης στην αγορά για βιώσιμα προϊόντα, υπηρεσίες και λύσεις, λόγω της περιβαλλοντικής συνείδησης των καταναλωτών, των εταιρικών δεσμεύσεων βιωσιμότητας και των κανονιστικών απαιτήσεων.
- Τεχνολογία και Καινοτομία: Εξελίξεις στις πράσινες τεχνολογίες, τις ανανεώσιμες πηγές ενέργειας, τις λύσεις κυκλικής οικονομίας, τις καθαρές μεταφορές και άλλες καινοτομίες που προωθούν την ανάπτυξη βιώσιμων επιχειρήσεων.
- Εκπαίδευση και Κατάρτιση: Ακαδημαϊκά ιδρύματα, προγράμματα κατάρτισης, εργαστήρια και πιστοποιήσεις που εφοδιάζουν τους επιχειρηματίες με γνώσεις και δεξιότητες σε θέματα πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας, βιώσιμων επιχειρηματικών πρακτικών και περιβαλλοντικής διαχείρισης.
- Υπηρεσίες Υποστήριξης: Εξειδικευμένοι πάροχοι υπηρεσιών, όπως νομικά γραφεία, εταιρείες συμβούλων, εταιρείες μάρκετινγκ και οργανισμοί μέτρησης επιπτώσεων, που ανταποκρίνονται στις ειδικές ανάγκες των πράσινων επιχειρηματιών.
- Αξιολόγηση και Μέτρηση των Επιπτώσεων: Εργαλεία, μεθοδολογίες και οργανισμοί που βοηθούν στη μέτρηση και αξιολόγηση του περιβαλλοντικού και κοινωνικού αντίκτυπου των πράσινων επιχειρήσεων, διευκολύνοντας τη λογοδοσία και τη διαφάνεια..
- Χώροι Συνεργασίας και Συνεργατικοί Κόμβοι: Φυσικοί χώροι που προσφέρουν περιβάλλοντα συνεργασίας, κοινόχρηστους πόρους και ευκαιρίες δικτύωσης για πράσινους επιχειρηματίες, προωθώντας τη δημιουργικότητα, την καινοτομία και τη διασταύρωση ιδεών.
- Ιστορίες Επιτυχίας και Πρότυπα Ρόλων: Εγκατεστημένες πράσινες επιχειρήσεις και εμπνευσμένοι επιχειρηματίες που έχουν επιτύχει σημαντική επιτυχία και αντίκτυπο, αποτελώντας παράδειγμα και πηγές έμπνευσης για τους επίδοξους πράσινους επιχειρηματίες.
Ένα από τα πιο σημαντικά ζητήματα εδώ είναι το ερώτημα: Πώς πρέπει να είναι μια τέτοια χαρτογράφηση; Ένα παράδειγμα μιας Χαρτογράφησης Οικοσυστήματος Πράσινης Επιχειρηματικότητας θα μπορούσε να περιλαμβάνει διάφορα ενδιαφερόμενα μέρη στο κέντρο της, με βέλη που να δείχνουν προς τους διάφορους πόρους που παρέχουν, όπως χρηματοδότηση, καθοδήγηση ή δικτύωση. Στο εξωτερικό στρώμα, θα μπορούσαν να υπάρχουν διάφορες προκλήσεις ή ευκαιρίες που επηρεάζουν το οικοσύστημα, με βέλη που δείχνουν προς τα διάφορα ενδιαφερόμενα μέρη ή πόρους που μπορούν να βοηθήσουν στην αντιμετώπιση αυτών των προκλήσεων ή στην αξιοποίηση αυτών των ευκαιριών. Αυτός ο τύπος χαρτογράφησης βοηθά να δείξει πώς το οικοσύστημα είναι διασυνδεδεμένο και πώς τα διάφορα στοιχεία του οικοσυστήματος μπορούν να συνεργαστούν για να υποστηρίξουν την πράσινη επιχειρηματικότητα.
Για παράδειγμα, επισκεφθείτε αυτόν τον σύνδεσμο: http://entrepreneurshipmapping.com/
Αυτός ο δικτυακός τόπος περιλαμβάνει ένα σχέδιο χαρτογράφησης του επιχειρηματικού συστήματος. Αυτή η χαρτογράφηση έχει δημιουργηθεί για να βοηθήσει στον εντοπισμό συγκεκριμένων επιχειρηματιών στο Ηνωμένο Βασίλειο. Ομολογουμένως, αυτοί δεν είναι συγκεκριμένα “πράσινοι επιχειρηματίες”, ωστόσο μια παρόμοια χαρτογράφηση με βάση αυτό το παράδειγμα θα μπορούσε να δημιουργηθεί με βάση το οικοσύστημα της πράσινης επιχειρηματικότητας.
Ένα άλλο παράδειγμα για το πώς μπορεί να μοιάζει μια τέτοια χαρτογράφηση παρουσιάζεται παρακάτω. Εδώ μπορείτε να δείτε τα βασικά στοιχεία που πρέπει να περιέχει κάθε τέτοια χαρτογράφηση:
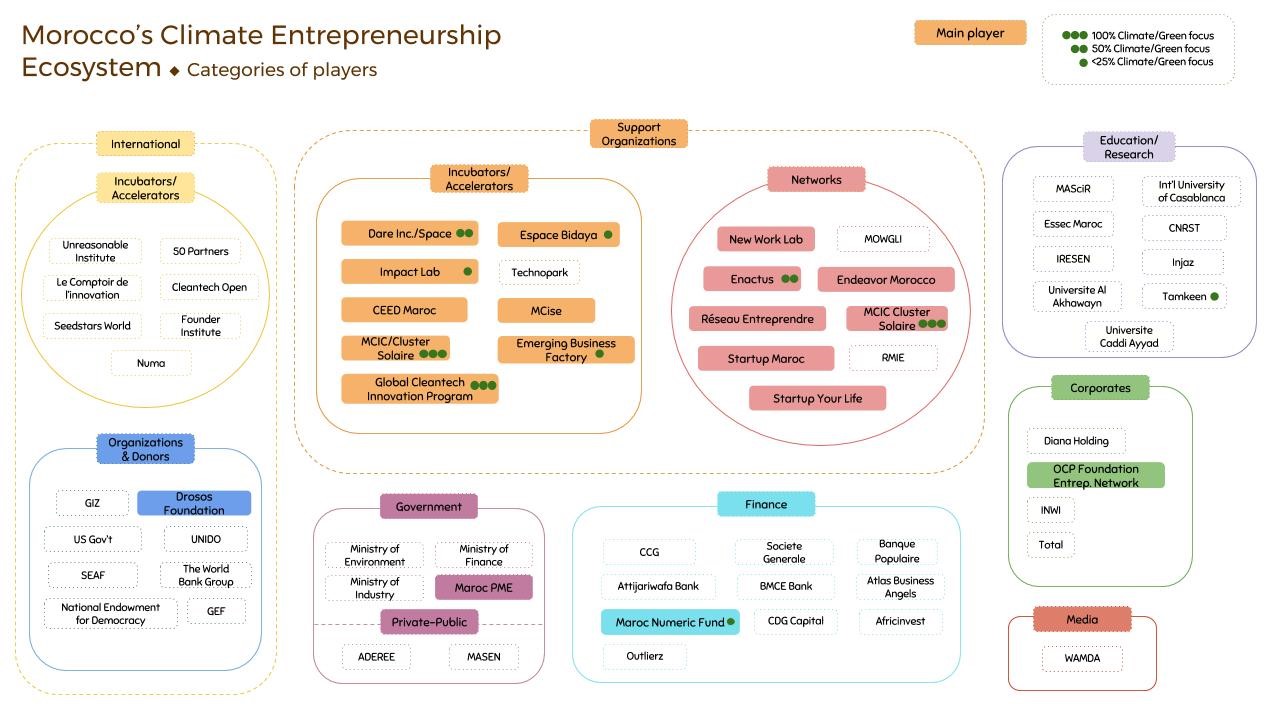 Πηγή: https://blogs.worldbank.org/psd/mapping-morocco-s-green-entrepreneurship-ecosystem
Πηγή: https://blogs.worldbank.org/psd/mapping-morocco-s-green-entrepreneurship-ecosystem

 English
English Română
Română Italiano
Italiano Polski
Polski Español
Español